第一章 React 入门
源码地址:https://gitee.com/szxio/zero-basic-learning-react
React 官网
中文网地址
https://react.docschina.org/
React 特点
- 声明式编码
- 组件化编码
- React Native 可以编写原生的应用
- 高效 (优秀的Diffing算法)
React 高效的原因
- 使用虚拟DOM不总是直接的操作页面真实DOM
- DOM Diffing 算法,最小化的页面重绘
Hello React
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
const DOM = <h1>Hello React</h1>
ReactDOM.render(DOM,document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
|
上面代码可以在页面中渲染出一个 Hello React
注意点:
- 必须先引入React核心库
react.development.js,然后再引入react-dom.development.js
- 必须将script标签的type设置为 text/babel,表明我们写的是 jsx
- jsx里面的dom不能添加引号
jsx多级嵌套标签语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <script type="text/babel">
const DOM = (
<h1>
<span>Hello React</span>
</h1>
)
ReactDOM.render(DOM,document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
|
使用一个小括号包起来表示一个整体,在括号内可以换行,像书写 html 一样编写虚拟DOM
jsx语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <style>
.title {
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
const data = "Hello,React"
const myId = "main"
const DOM = (
<div id={myId}>
<h1 style={{color:'white',fontSize:"25px"}}>
<span className="title">{data}</span>
</h1>
<h2>hello world</h2>
<input type="text" />
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(DOM,document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
|
jsx编写虚拟DOM时的语法
- 必须存在一个根元素节点
- 虚拟DOM中混入JS时使用{}引入
- 定义class时使用className来定义类样式,避免和es6中的class类语法冲突
- 定义行内样式时要使用
style={{ }} ,样式要使用驼峰写法
- 虚拟DOM的标签必须闭合
- 虚拟DOM的标签首字母规则
- 首字母小写时,react-dom 会直接吧该标签翻译成 html 中对应的标签
- 首字母大写时,react-dom 会认为这个标签是一个组件
jsx练习:动态循环数组
需求:使用jsx动态显示li
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
const liList = ["React","Vue","Angular"]
const DOM = (
<div>
<ul>
{
// jsx的花括号中只能包含js表达式
liList.map((item,index)=>{
return <li key={index}>{item}</li>
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(DOM,document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
|
jsx会自动便利数组内容到页面中
第二章 面向组件编程
定义函数式组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
function MyComponent(){
console.log(this);
return <h2>这是用函数定义的组件,适用于简单组件的定义</h2>
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
|
注意点:定义组件时,组件名称的首字母必须是大写
执行完 ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>...之后发生了什么?
- react找到了MyComponent组件
- 发现该组件是使用函数式声明的,则调用这个函数获取返回的虚拟DOM
- 然后将虚拟DOM转成真实DOM渲染到页面中
定义一个类式组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render(){
return <h2>我是用类定的组件</h2>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
注意点:
- 定义的类必须继承
React.Component 类
- 在自定义组件类中添加
render方法,返回虚拟DOM
上面代码中执行完ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>.... 后发生了什么事?
- 首先React解析组件时找到了
MyComponent组件
- 发现该组件是用类创建的,所以自动实例化出来一个这个类的对象
- 调用该类的render方法获取返回的虚拟DOM
- 翻译虚拟DOM成真实DOM到页面上
组件实例化的三大属性1_state
页面上内容可以根据状态的改变而改变
初始化状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
isHot: true
}
}
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state
return <h2>今天的天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'} </h2>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
添加事件绑定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
isHot: false
}
this.changeIsHot = this.changeIsHot.bind(this)
}
render() {
console.log(this);
const { isHot } = this.state
return <h2 onClick={this.changeIsHot}>今天的天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'} </h2>
}
changeIsHot() {
console.log(this);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById("app"))
|
上面代码中的几个注意点:
- React重写了所有原生的
onxxx方法,on后面的第一个单词要大写
onClick等于的方法名不能添加括号,否则会默认调用该方法,将该方法的返回值作为onClick的回调- 定义事件方法时,一定要注意
this指向问题
setState方法的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
isHot: false
}
this.changeIsHot = this.changeIsHot.bind(this)
}
render() {
console.log(this);
const { isHot } = this.state
return <h2 onClick={this.changeIsHot}>今天的天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'} </h2>
}
changeIsHot() {
console.log(this);
const {isHot} = this.state
this.setState({
isHot:!isHot
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById("app"))
|
setState方法的说明:setState方法接受一个对象,然后将这个对象合并到原来的state对象中,达到更新数据的操作。这个方法存放在React.component组件的原型上。当setState方法执行完后,会调用一次render方法,用来更新页面。
组件中几个方法的触发次数问题:
constructor方法:只会在页面加载时触发一次,用来实例化组件对象render方法:触发1+n次,1表示页面加载时触发一次,n表示state对象更新了几次- 自定义事件方法:点击了几次就会触发几次
state的简写形式
上面的代码写起来很繁琐,下面的代码时上面代码的简写形式,在开发中我们也推荐写下面的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
isHot: true
}
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state
return <h2 onClick={this.changeIsHot}>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h2>
}
changeIsHot = () => {
console.log(this);
const { isHot } = this.state
this.setState({
isHot: !isHot
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById("app"))
|
state问题总结
- render方法中的this是组件的实例对象
- 组件自定义方法的this是undefined,怎么解决?
- 在构造函数中使用 bind 方法改变自定义方法中的 this
- 使用箭头函数赋值
组件示例的三大属性2_props
props的基本使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
render(){
const {name,age} = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent name='李四' age='18'/>,document.getElementById("app"))
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent name='王五' age='21'/>,document.getElementById("app1"))
|
批量传递props属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
render(){
const {name,age} = this.props.userInfo
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
const userInfo = {
name:"李四",
age:18
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent userInfo={userInfo}/>,document.getElementById("app"))
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent {...userInfo}/>,document.getElementById("app2"))
|
对props属性进行限制
要想对props中的属性进行限制,首先引入prop-types.js,引入之后全局就多出了一个全局变量PropTypes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <div id="app"></div>
<div id="app2"></div>
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="../js/prop-types.js"></script>
|
然后使用 自定义组件名.propTypes={}的方式对props中的属性类型和是否必填进行限制
使用 自定义组件名.defaultProps={}的方式对props中的属性进行默认值设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, age, sex } = this.props
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
MyComponent.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
age: PropTypes.number,
sex: PropTypes.string,
speak:PropTypes.func
}
MyComponent.defaultProps = {
sex: "不男不女",
age:18,
}
let speak = ()=>{
console.log('说话方法');
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent name="张三" sex="男" age={18} />, document.getElementById("app"))
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent name="张三" speak={speak} />, document.getElementById("app2"))
|
限制类型列表
| 类型值 |
含义 |
| PropTypes.string |
字符串 |
| PropTypes.number |
数字类型 |
| PropTypes.func |
函数类型 |
| PropTypes.isRequired |
该属性必填 |
| PropTypes.string.isRequired |
设置属性类型是字符串并且必填 |
props限制规则的简写形式
首先复习一下类中的 static 关键字,这个关键字表示为静态的,在类属性前面声明了这个关键字后,这个属性会被添加到类的本身上面,不会被添加到类的实例化对象上。我们可以利用这个特性来简写props
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
static propTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string.isRequired,
sex:PropTypes.number
}
static defaultProps = {
age:18
}
render(){
console.log(this);
const {name,sex,age} = this.props
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
const userInfo = {
name:"liis",
sex:0
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent {...userInfo}/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
类式组件中construction的作用
通常,在 React 中,构造函数仅用于以下两种情况:
- 通过给
this.state 赋值对象来初始化内部 state
- 为事件处理函数绑定实例
如果我们希望在构造器中通过使用 this.props的方式来使用props,则在构造器中必须接收 porps,并且必须调用 super(props) 将props传递给React.Component,如果不接也不传,则可能出现this.props是undefined的bug
组件实例的三大属性3_refs
字符串形式的ref
ref 的作用是用来标记一个元素,和 id 的作用类似。React 会自动帮我们收集所有用 ref 标记的元素的真实 DOM 放到组件实例对象的 refs 属性中。使用时我们只需要通过使用 this.refs.xxx 来获取某个标记的元素DOM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
showData1 = ()=>{
const {input1} = this.refs
alert(input1.value)
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<input ref="input1" placeholder="点击按钮弹出信息"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1}>显示左侧信息</button>
<input placeholder="离焦点触发"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
回调形式的ref
关于字符串形式的 ref ,官方并不推荐我们使用,并且在未来的某个版本中可能会废弃掉。原因是效率不高。
所以下面是采用回调的形式来声明 ref。使用回调的形式后,React 在编译过程中会自动的调用我们写的回调函数,并且回调时会携带被标记元素的真实DOM。我们可以利用这个特点在回调方法中直接将真实DOM保存在组件的实例对象中。
注意:采用了回调形式创建ref后,React不会再往refs中添加ref
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
showData1 = ()=>{
console.log(this);
const {input1} = this
alert(input1.value)
}
showData2 = ()=>{
const {input2} = this
alert(input2.value)
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<input ref={cnode=> this.input1=cnode} placeholder="点击按钮弹出信息"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1}>显示左侧信息</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} ref={cnode=> this.input2=cnode} placeholder="离焦点触发"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
关于回调 refs 的说明
如果 ref 回调函数是以内联函数的方式定义的,在更新过程中它会被执行两次,第一次传入参数 null,然后第二次会传入参数 DOM 元素。这是因为在每次渲染时会创建一个新的函数实例,所以 React 清空旧的 ref 并且设置新的。通过将 ref 的回调函数定义成 class 的绑定函数的方式可以避免上述问题,但是大多数情况下它是无关紧要的。
代理示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
state = {
isHot:true
}
showInfo = ()=>{
let {isHot} = this.state
this.setState({
isHot:!isHot
})
}
render(){
const {isHot} = this.state
return (
<div>
<div>今天的天气很 {isHot ? '晴朗' : '阴沉'}</div>
<div>
<input ref={(cNode)=>{
// 在组件更新过程中,ref的回调会被执行两次,第一次回调参数是null,第二次是真正的DOM
this.input = cNode;
console.log('@',cNode);
}} placeholder="输入内容"/>
<button onClick={this.showInfo}>点击提示信息</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
上面的代码中在第一次运行时,ref 中的只会被触发一次,而在点击按钮更新页面后,ref 的回调会被触发两次,第一次参数是null,第二次才是DOM。
createRef 的使用
React.createRef 创建一个能够通过 ref 属性附加到 React 元素的 ref容器,这个容器只能装一个元素。专人专用,不能共享。在获取的时候必须通过 current 属性来获取 ref 标记的元素DOM。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class MyComponent extends React.Component{
input1 = React.createRef()
input2 = React.createRef()
showData1 = ()=>{
alert(this.input1.current.value);
}
showData2 = ()=>{
alert(this.input2.current.value)
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<input ref={this.input1} placeholder="点击按钮弹出信息"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1}>显示左侧信息</button>
<input ref={this.input2} onBlur={this.showData2} placeholder="离焦点触发"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
非受控组件
简单而言,非受控组件就是当我们提交数据时,才从页面中获取表单内容。这样的组件我们称为非受控组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class MyForm extends React.Component{
userName = React.createRef()
passWord = React.createRef()
submitForm = (event)=>{
console.log(event);
event.preventDefault()
const {userName,passWord} = this
alert(`用户名是:${userName.current.value},密码是:${passWord.current.value}`)
}
render(){
return (
<form onSubmit={this.submitForm}>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" ref={this.userName}/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" ref={this.passWord}/><br/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyForm/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
受控组件
可以观察下面的代码中并没有通过使用 ref 来获取输入框的值,而是通过 onChange 事件,当输入框的值发生变化时实时的将数据存入 state 中,当我们真正点击提交时再从 state 中获取表单数据。这种获取数据方式的组件称之为受控组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| class MyForm extends React.Component{
state = {
userName:"",
passWord:""
}
changeName = (e)=>{
this.setState({
userName:e.target.value
})
}
changePws = (e)=>{
this.setState({
passWord:e.target.value
})
}
submitForm = (event)=>{
event.preventDefault()
const {userName,passWord} = this.state
alert(`用户名是:${userName},密码是:${passWord}`)
}
render(){
return (
<form onSubmit={this.submitForm}>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" onChange={this.changeName}/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" onChange={this.changePws}/><br/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyForm/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
高阶函数和函数柯里化
高阶函数
什么是函数柯里化?如果一个函数符合下面2个规范中的任何一个,那么这个函数就是高阶函数
- 若A函数接收的参数是一个函数,那么这个函数就是高阶函数
- 若A函数的返回值仍然是一个函数,则这个函数就是高阶函数
常用的高阶函数有:setTimeout、Array.map()、Promise ……
函数柯里化
- 通过函数调用继续返回函数的方式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码方式
下面通过一个案例,体会函数柯力化。使用一个方法收集多个输入框数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class MyForm extends React.Component{
state = {
userName:"",
passWord:""
}
saveFormData = (key)=>{
return (e)=>{
console.log(key,e);
this.setState({
[key]:e.target.value
})
}
}
submitForm = (event)=>{
event.preventDefault()
const {userName,passWord} = this.state
alert(`用户名是:${userName},密码是:${passWord}`)
}
render(){
return (
<form onSubmit={this.submitForm}>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" onChange={this.saveFormData('userName')}/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" onChange={this.saveFormData('passWord')}/><br/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyForm/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
上面的代码中,onChange 接收一个方法作为回调。saveFormData 方法由于添加了小括号,所以在第一次编译时会被自动执行,但是由于这个方法的返回值也是一个函数,所以onChange 的回调还是一个函数。
第三章 React生命周期(旧版本)
生命周期初体验
通过完成如下案例:在页面挂载完成后启动一个计时器,每隔200毫秒吧文字大小增加1像素值,当大小超过40像素值时,文字大小重新变回12像素。点击关闭按钮时,卸载组件。组件卸载前清空一下计时器。
效果图

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| class LifeComponent extends React.Component{
state = {
fontSize:12
}
unMount = ()=>{
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById("app"))
}
componentDidMount(){
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
let {fontSize} = this.state
fontSize += 1
if(fontSize >= 40) fontSize = 12
this.setState({
fontSize:fontSize
})
}, 200);
}
componentWillUnmount(){
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
render(){
let {fontSize} = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2 style={{fontSize:fontSize + 'px',transition:'1s'}}>我会自己变大变小</h2>
<button onClick={this.unMount}>关闭</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<LifeComponent/>,document.getElementById("app"))
|
上面的案例中用到的生命周期有
| 函数名 |
含义 |
componentDidMount |
组件挂载完成后触发 |
componentWillUnmount |
组件卸载前触发 |
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode( document.getElementById() ) |
卸载指定的组件 |
组件声明周期
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class Count extends React.Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
console.log('Count - constructor');
}
state = {
count: 0
}
add = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
componentWillMount(){
console.log('Count - componentWillMount');
}
render() {
console.log('Count - render');
return (
<div>
<h2>当前的和为:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button>
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log('Count - componentDidMount');
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count />, document.getElementById("app"))
|
组件挂载时流程:
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
constructor |
最先调用构造器方法 |
componentWillMount |
组件将要挂载时触发 |
render |
组件挂载触发 |
componentDidMount |
组件挂载完成后触发 |
组件销毁时流程
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
componentWillUnmount |
组件将要销毁时触发 |
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode( document.getElementById() ) |
卸载指定的组件 |
组件的setState流程
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
shouldComponentUpdate |
定义组件是否可以被更新,返回布尔值,不写默认返回true,表示可以更新状态 |
componentWillUpdate |
组件将要更新 |
render |
组件更新方法 |
componentDidUpdate |
组件更新完成方法 |
forceUpdate 强制更新
forceUpdate方法存放在React的原型链上,可以在代码中直接通过this.来调用。这个方法可以在不更新状态的前提下更新组件
1
2
3
4
|
this.state.count = 10
this.forceUpdate()
|
执行完this.forceUpdate方法后,会依次触发下面的生命周期钩子函数
componentWillUpdate 组件将要更新render 编译组件componentDidUpdate 组件更新完成
父子组件传参时的更新流程
当父组件给子组件通过props传参时,会触发componentWillReceiveProps方法,该方法可以接收到传递过来的props。但是,这个方法在初始化传递时不会调用,只会在传递新的props时调用。传递过来之后会依次触发更新流程上的钩子函数。
首先定义父组件。点击按钮切换状态并将状态值传递给子组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class A extends React.Component{
state = {
cart:'奔驰'
}
changeCart = ()=>{
this.setState({
cart:'奥拓'
})
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<button onClick={this.changeCart}>点击换车</button>
{/* 在父组件中直接写子组件的名称即可表示父子组件关系 */}
<B cart={this.state.cart}/>
</div>
)
}
}
|
然后再组件中接收这个参数并展示。在点击按钮后回触发componentWillReceiveProps回调方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class B extends React.Component{
componentWillReceiveProps(props){
console.log(props);
console.log('组件将要接收新的props时触发 - componentWillReceiveProps');
}
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('是否更新:True');
return true
}
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log('将要更新');
}
render(){
console.log('编译');
return(
<h3>当前的车辆是:{this.props.cart}</h3>
)
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log("更新完成");
}
}
|
注意:componentWillReceiveProps方法只会在传递新的props时触发,在页面加载时不会触发
声明周期总结
初始化阶段
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
| construction |
类的构造器方法 |
| componentWillMount |
组件将要挂载 |
| render |
编译组件 |
| componentDidMount |
组件挂载完成 |
更新阶段
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
| shouldComponentUpdate |
获取状态是否可以更新,默认返回true |
| componentWillUpdate |
组件将要更新 |
| render |
更新状态 |
| componentDidUpdate |
组件更新完成 |
卸载阶段
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
| componentWillUnmount |
组价将要卸载 |
| ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode( ) |
卸载指定的组件 |
父组件传参
| 函数名 |
函数含义 |
| componentWillReceiveProps |
组件将要接收新的props时触发 |
声明周期流程图

第四章 React声明周期(新版本)
新旧生命周期区别
新版本中即将废弃三个生命周期函数,分别如下
componentWillMountcomponentWillUpdatecomponentWillReceiveProps
在17.x版本中,这三个生命周期仍然可以使用,但是会在控制台报警告,我们需要添加UNSAFE_前缀来取消警告。但是在未来的某个版本中可能必须要添加UNSAFE_前缀才能使用它们。这是因为React在做异步渲染,这三个函数可能会被误解和滥用,以至于出现bug,所以我们应该避免使用它们。
新版本中又新增了两个生命周期函数,分别如下
static getDerivedStateFromPropsgetSnapshotBeforeUpdate
getDerivedStateFromProps
该方法在 constructor 之后 render 之前触发。并且要求是一个静态方法,所以要在声明前添加 static 关键字。该方法必须返回 null ,或者衍生状态对象,如果返回了衍生状态对象,则该状态将无法被修改,只能通过 props 来修改状态。
此方法适用于罕见的用例,即 state 的值在任何时候都取决于 props。例如,实现 <Transition> 组件可能很方便,该组件会比较当前组件与下一组件,以决定针对哪些组件进行转场动画。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class Count extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
console.log('constructor');
}
state = {
count:19
}
addCount = () =>{
let {count} = this.state
this.setState({
count:++count
})
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props){
console.log('getDeriveStateFromProps',props);
return props
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<h2>数据和为:{this.state.count}</h2>
<h3>姓名:{this.state.name}</h3>
<button onClick={this.addCount}>点击+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count name={'李四'}/>,document.getElementById('app'))
|
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
该方法在 render 后、componentDidUpdate 之前触发,必须返回一个null或者一个快照,快照可以是任何类型的数据,返回的数据由 componentDidUpdate 函数的第三个参数接收
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class Count extends React.Component{
state = {
count:0
}
add = ()=>{
let {count} = this.state
count++
this.setState({
count:count
})
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(){
return 'songzx'
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<h2>和是:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>增加</button>
</div>
)
}
componentDidUpdate(prevprops,prevstate,snapshot){
console.log(prevprops);
console.log(prevstate);
console.log(snapshot);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count count={9}/>,document.getElementById('app'))
|
新生命周期图
 .png)
.png)
第五章 遍历时key的作用
虚拟DOM中key的作用
- 简单的说:key时虚拟DOM对象的标识,在更新显示时,key起着及其重要的作用
- 详细的说:当状态中的数据发生变化时,react会根据【新数据】生成【新的虚拟DOM】,随后React【新虚拟DOM】和【旧虚拟DOM】会进行 diff 比较,比较规则如下:
- 旧虚拟DOM会找到和新虚拟DOM中key一样的DOM
- 若虚拟DOM中的内容没有变化,则复用之前的旧虚拟DOM
- 若虚拟DOM中的内容变化了,则生成新的真实DOM替换原来的DOM
- 旧虚拟DOM中没有找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key
用index索引值作为key可能会发生的问题
- 若对数据进行:逆序添加,逆序删除等操作时,会产生没有必要的正式DOM更新。界面效果展示虽然没有问题,但是效率低
- 如果结构中包含输入类的DOM,会产生DOM更新错误,界面展示都会出现问题
- 注意:如果不存在对数据进行逆序添加,逆序删除等破坏顺序的操作时,进用于数据的展示,则用index作为key也是没有问题的
如何选择key
- 最好使用每条数据中的唯一值作为key。例如id、身份证号、学号等
- 如果确定只是简单的数据展示,则用index也是没问题的
第六章 React 脚手架
React 脚手架
- xxx 脚手架:用来帮助程序员快速创建一个基于 xxx 库的模板项目
- 包含了所有需要的配置(语法检查,jsx编译,devServer)
- 下载好了相关的依赖
- 可以直接运行一个简单效果
- react 提供了一个用于创建 react 项目的脚手架库: react-react-app
- 项目的整体架构为:react + webpack + es6 + eslint
- 使用脚手架开发的项目特点:模块化、工程化、组价化
创建和启动
首先全局安装 react
1
| npm install -g create-react-app
|
创建项目命令
启动项目
启动成功后可以看到如下页面

public/index.html文件的说明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
<meta
name="description"
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
/>
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/logo192.png" />
<link rel="manifest" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/manifest.json" />
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>
|
src目录下文件说明

实现一个简单的Hello组件
在开始之前我们将src文件夹下面的文件全部剪切走,重新开始编写我们的scr文件下的内容
首先编写src/index.js文件,这个文件是我们整个项目的入口文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import App from "./App"
ReactDOM.render(<App />,document.getElementById('root'))
|
然后新建src/App.js文件,并编写如下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>Hello React</div>
);
}
}
|
然后再src目录下新建components文件夹,用来放置我们开发的所有组件。
接着在components文件夹下新建Hello/index.jsx和Hello/index.css文件
Hello/index.jsx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./index.css"
export default class Hello extends Component {
render() {
return <h2 className="title">Hello React</h2>;
}
}
|
Hello/index.css
1
2
3
| .title{
background-color: orange;
}
|
其次我们在components文件夹中再新建Welcome/index.jsx和Welcome/index.css
Welcome/index.jsx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./index.css"
export default class Welcome extends Component {
render() {
return <h2 className="demo">Welcome</h2>;
}
}
|
Welcome/index.css
1
2
3
| .demo{
background-color: skyblue;
}
|
最后我们在App.js中引入Hello组件和Welcome组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import React, { Component } from "react";
import Hello from "./components/Hello";
import Welcome from "./components/WelCome";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Hello />
<Welcome />
</div>
);
}
}
|
最终的页面效果

上面的代码中有几个细节点:
- 声明组件时文件名首字母要大写
- 通常我们将组件的后缀设置为
jsx,普通的业务文件后缀为js
React.Component组件可以简写为import React, { Component } from "react";
样式文件模块化
当我们在两个组件中使用了相同的样式类名,会导致后引入组件的样式覆盖之前引入组件的样式。我们可以通过下面的方法来设置样式文件的模块化
首先重命名css文件的后缀固定设置为xxx.model.css
然后再组件中使用具名导入的形式引入定义的css文件
使用的时候要使用花括号的形式使用类名,例如:className={welcome.title}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import welcome from "./index.module.css"
export default class Welcome extends Component {
render() {
return <h2 className={welcome.title}>Welcome</h2>;
}
}
|
React相关插件
插件名称
1
| ES7 React/Redux/GraphQL/React-Native snippets
|
快捷键
rcc,快速新建类式组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class FileName extends Component {
render() {
return <div>$2</div>
}
}
|
rfc,快速新建方法组件
1
2
3
4
5
| import React from 'react'
export default function $1() {
return <div>$0</div>
}
|
第七章 实现 ToDoList 案例
拆分组件
首先看页面,我们可以根据页面结构将页面分成几个组件


代码目录结构如下

在App组件中引入Header,List,Footer组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import Header from "./components/Header";
import List from "./components/List";
import Footer from "./components/Footer";
import "./base.css";
import appcss from "./app.module.css";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className={appcss.todoContent}>
<Header />
<List />
<Footer />
</div>
);
}
}
|
然后再List组件中引入Item组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import listcss from "./index.module.css";
import Item from "../Item";
export default class index extends Component {
render() {
return (
<ul className={listcss.listMain}>
<Item />;
</ul>
);
}
}
|
父传子
父组件给子组件传值,直接在 App 组件中通过 props 给子组件传值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| state = {
todos: [
{
id: "001",
name: "吃饭",
done: true,
},
{
id: "002",
name: "睡觉",
done: false,
},
{
id: "003",
name: "打代码",
done: true,
},
],
};
.....
<List todos={todos} />
|
然后再 List 组件中从 this.props 对象中获取父组件传递过来的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
render(){
const { todos } = this.props;
return (
<ul className={listcss.listMain}>
{/* 遍历循环 Item 组件 */}
{todos.map((todo) => {
// {...todo} 将这个todo都传递给item组件,这种是简写形式
return <Item key={todo.id} {...todo}/>;
})}
</ul>
);
}
|
子传父
我们可以利用回调函数的特性,来实现子组件给父组件传值
首先在父组件中定义一个方法,然后通过props 将这个方法传递给子组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
addTodo = (todoObj) => {
const { todos } = this.state;
todos.unshift(todoObj);
this.setState({
todos: todos,
});
};
......
<Header addTodo={this.addTodo} />
|
然后在子组件中调用这个方法并传递值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
handerKeyUp = (event) => {
const { keyCode, target } = event;
if (keyCode !== 13) return;
if (target.value.trim() === "") {
alert("请输入待办项目");
return;
}
let todoObj = {
id: nanoid(),
name: target.value,
done: false,
};
this.props.addTodo(todoObj);
target.value = "";
};
render() {
return (
<div className={headercss.headerMain}>
<input
onKeyUp={this.handerKeyUp}
type="text"
placeholder="请输入代办事项,按回车确定"
/>
</div>
);
}
|
nanoid 库的使用
nanoid 可以帮助我们生成一个全球唯一的uuid。
安装
使用,注意 nanoid 是采用分别导出的形式导出了一个 nanoid 方法
1
2
3
| import { nanoid } from "nanoid";
nanoid()
|
添加鼠标移入移出事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
state = {
flag: false,
};
handerEnter = (flag) => {
return () => {
this.setState({
flag: flag,
});
};
};
render() {
const { name, done } = this.props;
const { flag } = this.state;
return (
<li
style={{ backgroundColor: flag ? "#ddd" : "white" }}
onMouseEnter={this.handerEnter(true)}
onMouseLeave={this.handerEnter(false)}
className={itemcss.itemMain}
>
<input type="checkbox" defaultChecked={done} />
<div>{name}</div>
<button
style={{ display: flag ? "block" : "none" }}
className={itemcss.deleteBtn}
>
删除
</button>
</li>
);
}
|
脚手架添加propTypes
默认脚手架没有安装prop-types,需要我们手动安装
使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import PropTypes from "prop-types";
static propTypes = {
addTodo: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
};
|
第八章 配置代理解决跨域
设置代理方式1
配置代理前我们需要启动一个后台服务器,我们可以用 node + express快速搭建一个后台服务
安装 express
1
| npm install express --save
|
新建 index1.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| var express = require("express");
var app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(req);
next()
})
app.get("/students", (req, res) => {
let query = [
{
id: "001",
name: "法外狂赌张三",
age: 18,
},
{
id: "002",
name: "李四",
age: 20,
},
];
res.send(query);
});
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("服务已启动,地址:http://localhost:5000");
});
|
然后运行 node index1.js 启动后台服务,启动效果如下
1
2
| PS D:\mygitee\node后端> node .\index1.js
服务已启动,地址:http://localhost:5000
|
然后在我们的 React 项目中安装 axios
1
| npm install axios --save
|
接着在 App.js 中发送请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import axios from "axios"
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return <button onClick={this.getStatusData}>点击获取数据</button>;
}
getStatusData = ()=>{
axios.get("http://localhost:5000/students").then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
}
}
|
这时点击按钮发送请求会在控制台看到如下错误

这时受到浏览器的同源策略影响,产生的请求跨域。我们可以通过配置代理的方式来解决。
找到项目根目录下的 package.json 文件,在跟结构上添加如下代码

proxy后面跟上后台服务地址,注意不要加具体的接口名字,只要添加http前缀和域名即可,之后重启项目
我们在请求时要将原本的5000端口换成3000,修改App.js文件
1
2
3
| axios.get("http://localhost:3000/students").then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
|
然后再次点击请求会发现正常拿到数据

说明:
- 优点:配置简单,前端请求资源时不需要添加前缀即可请求
- 缺点:不能配置多个,只能配置一个
- 工作方式:上述方法配置代理,当请求了3000不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转给5000,优先匹配前端资源
设置代理方式2
1.第一步 :创建代理配置文件,注意该文件名为固定,不可更改
1
| 在src目录下新建 src/setupProxy.js
|
2.第二步 编写 setupProxy.js 文件的配置规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| const proxy = require("http-proxy-middleware");
module.exports = function (app) {
app.use(
proxy("/api1", {
target: "http://localhost:5000",
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { "^/api1": "" },
}),
proxy("/api2", {
target: "http://localhost:5001",
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { "^/api2": "" },
})
);
};
|
3.第三步 重启项目
4.第四步 修改 App.js 中的请求前缀
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.getStatusData}> 获取学生数据 </button>
<button onClick={this.getCartData}> 获取汽车数据 </button>
</div>
);
}
getStatusData = () => {
axios.get("/api1/students").then((res) => {
console.log(res.data);
});
};
getCartData = () => {
axios.get("/api2/carts").then((res) => {
console.log(res.data);
});
};
}
|
5.效果展示,点击两个按钮访问不同的服务器,均能获取到数据

第九章 开发GitHub搜索接口
新建node服务
首先在空白文件夹初始化npm
按照提示会生成一个 package.json 文件
然后安装 express
然后再安装 axios
然后再根目录新建 search.js,编写如下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| const app = require('express')()
const axios = require('axios')
app.get("/search/users", (req, res) => {
const { q } = req.query
axios({
url: 'https://api.github.com/search/users',
params: { q }
}).then(response => {
res.json(response.data)
}).catch(() => {
res.json({
"total_count": 19,
"incomplete_results": false,
"items": [{
"login": "songzx",
"id": 3830378,
"node_id": "MDQ6VXNlcjM4MzAzNzg=",
"avatar_url": "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/3830378?v=4",
"gravatar_id": "",
"url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx",
"html_url": "https://github.com/songzx",
"followers_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/followers",
"following_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/following{/other_user}",
"gists_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/gists{/gist_id}",
"starred_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/starred{/owner}{/repo}",
"subscriptions_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/subscriptions",
"organizations_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/orgs",
"repos_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/repos",
"events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/events{/privacy}",
"received_events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx/received_events",
"type": "User",
"site_admin": false,
"score": 1
}, {
"login": "songzxDev",
"id": 6290650,
"node_id": "MDQ6VXNlcjYyOTA2NTA=",
"avatar_url": "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/6290650?v=4",
"gravatar_id": "",
"url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev",
"html_url": "https://github.com/songzxDev",
"followers_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/followers",
"following_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/following{/other_user}",
"gists_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/gists{/gist_id}",
"starred_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/starred{/owner}{/repo}",
"subscriptions_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/subscriptions",
"organizations_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/orgs",
"repos_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/repos",
"events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/events{/privacy}",
"received_events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzxDev/received_events",
"type": "User",
"site_admin": false,
"score": 1
}, {
"login": "songzx0309",
"id": 3347681,
"node_id": "MDQ6VXNlcjMzNDc2ODE=",
"avatar_url": "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/3347681?v=4",
"gravatar_id": "",
"url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309",
"html_url": "https://github.com/songzx0309",
"followers_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/followers",
"following_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/following{/other_user}",
"gists_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/gists{/gist_id}",
"starred_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/starred{/owner}{/repo}",
"subscriptions_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/subscriptions",
"organizations_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/orgs",
"repos_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/repos",
"events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/events{/privacy}",
"received_events_url": "https://api.github.com/users/songzx0309/received_events",
"type": "User",
"site_admin": false,
"score": 1
}]
})
})
})
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log('服务已经启动,访问地址 http://localhost:5000/search/users?q=xxx');
})
|
之后在根目录输入启动命令
启动成功如下:

请求接口可以看到接口返回的数据

第十章 组件之间的互相通信
父子通信
首先在 APP 组件中引入了 Header 和 List 组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| render() {
return (
<div className="app-main">
<Header />
<List />
</div>
);
}
|
Header 组件点击搜索获取到数据后如何给自己的父组件 App 呢?
首先在父组件 App 上定义一个 setStateUsers 方法,然后通过 props 将这个方法传递给子组件 header
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| export default class App extends Component {
state = {
users: []
}
setStateUsers = (users) => {
this.setState({
users
})
}
render() {
return (
<div className="app-main">
<Header setStateUsers={this.setStateUsers} />
<List users={this.state.users}/>
</div>
);
}
}
|
然后再子组件 Header 中点击搜索获取到数据后调用props 上的方法传递数据给App
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
searchUsers = () => {
const nameVal = this.inputEle.current.value
if (!nameVal) {
alert('姓名不允许为空')
return
}
axiox.get(`/api1/search/users?q=${nameVal}`).then(res => {
this.props.setStateUsers(res.data.items)
})
};
|
这样父组件App 上定义的 setStateUsers 会被触发并且可以接受到 子组件 Header 传递过来的 users 数据,然后通过 props 传递给另外一个子组件 List ,从而完成数据的展示
消息订阅和发布
完成这个功能我们需要第三方的插件,这里我们采用 pubsub-js,首先安装到我们的项目中
该插件采用发布订阅模式来实现组件间通信。
我们来改进上面的传值方法,让 Header 组件和 List 组件直接进行通信,不通过 App 组件进行中转
首先修改 App ,既然来让两个兄弟组件进行通信,那么App 组件就不需要维护状态和方法了,改进后代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className="app-main">
<Header />
<List />
</div>
);
}
}
|
然后在 Header 组件中发布消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import headercss from "./index.module.css";
import axiox from "axios"
import PubSub from "pubsub-js";
export default class Header extends Component {
inputEle = React.createRef()
searchUsers = () => {
const nameVal = this.inputEle.current.value
if (!nameVal) {
alert('姓名不允许为空')
return
}
axiox.get(`/api1/search/users?q=${nameVal}`).then(res => {
PubSub.publish('users', res.data.items)
})
};
render() {
return (
<div className={headercss.main}>
<div className={headercss.searchbox}>
<h3>Search Gitee Users</h3>
<div className={headercss.inputbox}>
<input ref={this.inputEle} type="text" placeholder="请搜索" />
<button onClick={this.searchUsers}>点击搜索</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
|
发布消息时使用 PubSub.publish('users', res.data.items) 方法,这个方法接受两个参数:
- users:声明发布的消息名称,然后订阅消息时监听这个名称,当消息发布后会触发监听消息的回调
- res.data.items:发布消息要发送的数据
最后在 List 组件中监听消息,监听到消息后更新状态渲染页面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import listcss from "./index.module.css"
import Item from "../Item"
import PubSub from 'pubsub-js';
export default class List extends Component {
state = {
users: []
}
componentDidMount() {
PubSub.subscribe('users', (_, data) => {
this.setState({
users: data
})
})
}
render() {
const { users } = this.state
return (
<div className={listcss.main}>
{
users.map(item => {
return (
<Item key={item.id} item={item} />
)
})
}
</div>
)
}
}
|
订阅消息调用 PubSub.subscribe('users',(msg.data)=>{ }),subscribe 方法同样接受两个参数:
- 第一个参数是要监听那个消息,这个名称要和发布消息时定义的名称一致
- 第二个参数是一个函数,当消息发布成功后会触发这个函数,这个函数有两个参数
第十一章 使用 fetch 发送请求
介绍
fetch 是不依赖第三方的原生自带的一个请求方法,它和之前常用的 XMLHttpRequest 是一个级别的,不和 jquery、axios 一个级别,因为这些库都只是对 XMLHttpRequest 的封装。 我们一起来学习一下这个 fetch 到底怎么使用的吧
使用 fetch 发送 GET 请求
标准写法,有待优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| fetch(`/api1/search/users?q=${nameVal}`).then(res => {
return res.json()
}).then(res => {
PubSub.publish('users', res.items)
}).catch(err => {
alert(JSON.stringify(err))
})
|
上面的写法还可以进一步优化,使用 async await 语法来优化上述代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| try {
const response = await fetch(`/api1/search/users?q=${nameVal}`)
const result = await response.json()
PubSub.publish('users', result.items)
} catch (error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error))
}
|
await 只能够接收到成功的返回,并不能处理错误的返回,所以我们使用 try cathc 来处理异常结果
使用 fetch 发送 POST 请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| fetch('https://...', {
method: 'post',
body: JSON.stringify(base),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}).then(function(data) {
})
|
第十二章 React 路由
什么是SPA单页面
- 整个页面只有一个完整的页面
- 点击页面的链接不会刷新整个页面,只会做页面的局部更新
- 数据通过ajax获取,前端异步显示
什么是路由
- 一个路由就是一个映射关系
- key为路径,value可能是function,也可能是一个component
前端路由的工作原理
- 前端路由是靠浏览器中的BOM对象身上的history来实现的
- 我们每次点击菜单进行跳转时会往history的栈结构中压入一条数据
- history是H5提出的一个新语法
- 不用history路由还有一种hasHistory,类似于锚点
认识 react-router-dom
react-router-dom 是React官方维护的专门用来开发单页面应用的插件。
安装,目前官方的插件版本已经升级到的6.0,写法和5.0有些不同,学习阶段我们以5.2.0版本为例来学习
1
| npm i react-router-dom@5.2.0 --save
|
安装成功后修改 src\index.js 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom"
import App from "./App";
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
|
接着修改App.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Link, Route,Routes } from "react-router-dom"
import Home from "./components/Home"
import About from "./components/About"
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>
{/* React中使用Link实现组件跳转 */}
<Link className="list-group-item" to='/home'>Home</Link>
<Link className="list-group-item" to='/about'>About</Link>
</div>
<div>
{/* 注册路由 */}
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
|
总结:
路由区要使用 Link 标签来写,并使用 to 属性标识要跳转的路径
展示区要使用 Route 标签来展示显示那个具体的组件
效果演示,可以看到点击不同的菜单,路径会发生变化,但是页面不会刷新

路由组件和一般组件
写法不同
- 一般组件:
<Demo></Demo>
- 路由组件:
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
存放的位置不同
- 一般组件推荐放在
components 文件夹下
- 路由组件推荐放在
pages 文件夹下
介绍的 props 不同
一般组件不会接收到默认的 props
路由组件会接收到默认的 props
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| history:
go: ƒ go(n)
goBack: ƒ goBack()
goForward: ƒ goForward()
push: ƒ push(path, state)
replace: ƒ replace(path, state)
location:
pathname: "/about"
search: ""
state: undefined
match:
params: {}
path: "/about"
url: "/about"
|
NavLink 的使用
使用 NavLink 标签替换 Link 标签后,当我们点击某个连接时,会默认给这个连接添加一个 active 的样式类
1
2
3
4
| import { NavLink, Route } from "react-router-dom"
<NavLink activeClassName="select" className="list-group-item" to='/home'>Home</NavLink>
<NavLink activeClassName="select" className="list-group-item" to='/about'>About</NavLink>
|
我们也可以使用 activeClassName 来自定义点击时添加什么类名。
1
2
3
4
| .select{
background-color: orange !important;
color: white !important;
}
|
这里有个小小的坑,就是添加样式时要提高权重值,避免其他UI库的影响。
实现效果

封装 NavLink
当我们页面中有多个 NavLink 标签时,就需要定义多个 activeClassName 和 className,这就造成了代码的重复,接下我们对 NavLink 进行一个二次封装,来简化代码
新建 src\components\MyNavLink.jsx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { NavLink } from "react-router-dom"
export default class MyNavLink extends Component {
render() {
return <NavLink activeClassName="select" className="list-group-item" {...this.props}/>
}
}
|
MyNavLink 组件中通过 {...this.props} 批量的接收到 props 值,并且添加到 NavLink 标签上
然后修改 App 组件
1
2
3
4
5
| import MyNavLink from "./components/MyNavLink";
{}
<MyNavLink to='/home'>Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to='/about'>About</MyNavLink>
|
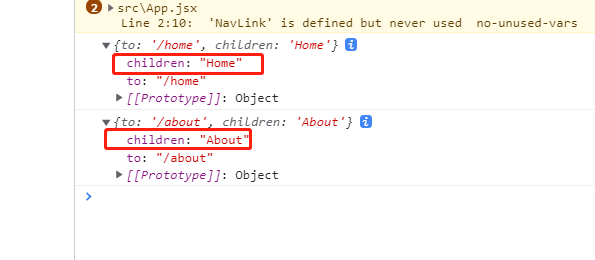
这里我们在 MyNavLink 标签中添加的 Home 和 About 也会被作为 props 参数传递个 MyNavLink,只不过名字为默认的 children
我们可以在 MyNavLink 组件中打印一下传递过来的参数

通过控制台可以发现 children 刚好就是我们在标签中写的值。这样我们通过批量接收 props 的值就可以实现 NavLink 的效果,同时也简化我们的代码。
Switch 组件的使用
react 在匹配 Route 时,如果匹配到了一个会继续往后匹配,并且会把所有匹配到的内容展示出来,这样效率不会太高,怎么才能设置匹配到一个组件后就停止匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import { Route, Switch } from "react-router-dom"
<Switch>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/about" component={Test} />
</Switch>
|
但是通常情况下,path 和 component 是一一对应的,不会出现一对多的情况。
解决样式丢失问题
首先我们在所有的路径前面添加一个固定的前缀
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <MyNavLink to='/songzx/home'>Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to='/songzx/about'>About</MyNavLink>
<Switch>
{/* 注册路由 */}
<Route path="/songzx/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/songzx/about" component={About} />
</Switch>
|
这样我们在进行页面点击时会出现下面的效果

通过动画可以看到,页面在进行切换时样式正常显示,但是在刷新后,样式会丢失,这是因为我们添加看一个前缀后,请求css的路径就会变成下面的地址
1
| http://localhost:3000/songzx/css/bootstrap.css
|
http://localhost:3000 对应我们的 public 文件夹,但是 public 文件夹下面并没有 songzx 文件夹,所有导致 css 文件找不到。
解决方法一(推荐):
修改 public\index.html 文件中的 css 引入的路径,将原本的 ./ 换成 / ,这样直接从根目录下查找该 css 文件。

解决方法二:
修改 public\index.html 文件中的 css 引入的路径,将原本的 ./ 换成 %PUBLIC_URL%/

解决方法三(不推荐):
将 BrowserRouter 路由模式换成 HashRouter 路由模式,但是这样做后,浏览器路径上会多出一个 # 号,不美观

我们按照第一种解决方法修改后,再来看页面刷新后的效果,点击刷新后,css样式不会丢失

路由的严格匹配
在 Route 标签中添加 exact 属性即可开启路由严格匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| {}
<MyNavLink to='/home'>Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to='/about/a/b'>About</MyNavLink>
{}
<Switch>
{}
<Route exact path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route exact path="/about" component={About} />
</Switch>
|
开启了严格匹配后必须路径和路由一摸一样才能被匹配到。因此在不影响页面显示的情况下,不建议开启严格匹配模式。
redirect重定向路由
1
2
3
4
| import { Route, Switch, Redirect } from "react-router-dom"
{}
<Redirect to="/home" />
|
Redirect 重定向可以理解为一个 “兜底” 的人
嵌套路由
首先在 Home 文件夹下添加 News 和 Message 两个页面,然后修改 src\pages\Home\index.jsx 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import MyNavLink from "../../components/MyNavLink"
import { Switch, Route, Redirect } from "react-router-dom"
import News from "./News"
import Message from "./Message"
export default class Home extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li>
<MyNavLink to="/home/news">News</MyNavLink>
</li>
<li>
<MyNavLink to="/home/message">Message</MyNavLink>
</li>
</ul>
<Switch>
<Route path="/home/news" component={News} />
<Route path="/home/message" component={Message} />
<Redirect to="/home/news" />
</Switch>
</div>
)
}
}
|
效果演示

向路由组件传递 params 参数
修改 src\pages\Home\Message\index.jsx 文件代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Detailed from './Detailed'
import { Link, Route } from "react-router-dom"
export default class Message extends Component {
state = {
msgList: [
{
id: "01",
title: "消息1",
content: "我爱你,中国"
},
{
id: "02",
title: "消息2",
content: "我爱你,React"
},
{
id: "03",
title: "消息3",
content: "我爱你,自己"
},
]
}
render() {
const { msgList } = this.state
return (
<div>
{
msgList.map(item => {
return (
<div key={item.id}>
<Link to={`/home/message/detailed/${item.id}/${item.title}/${item.content}`}> {item.title}
</Link>
</div>
)
})
}
<hr />
<Route path="/home/message/detailed/:id/:title/:content" component={Detailed} />
</div>
)
}
}
|
在接收参数的地方通过 :id/:title/:content 的方式定义了我们接收参数的 key
然后在 Detailed 组件中接收参数并使用,修改 src\pages\Home\Message\Detailed\index.jsx 组件如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Detailed extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props);
const { id, title, content } = this.props.match.params
return (
<div>
<p>id:{id}</p>
<p>title:{title}</p>
<p>content:{content}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
|
效果

向路由组件传递 search 参数
首先定义路由,link 传参时要指定好 key 和 value,Route 在接收路径时不需要在接收参数
1
2
3
4
5
| <Link to={`/home/message/detailed/?id=${item.id}&title=${item.title}&content=${item.content}`}>
{item.title}
</Link>
<Route path="/home/message/detailed" component={Detailed}></Route>
|
然后再 Detailed 组件中接收
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import qs from "querystring"
export default class Detailed extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props);
const { search } = this.props.location
const { id, title, content } = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
return (
<div>
<p>id:{id}</p>
<p>title:{title}</p>
<p>content:{content}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
|
这里我们解析字符串格式的参数引入了一个React 脚手架中自带的一个库,querystring,这个库有两个方法:parse 和 stringify
1
2
3
4
5
| let params = 'id=1&name=李四'
console.log(qs.parse(params));
let params2 = { carName:"bwm",price:199 }
console.log(qs.stringify(params2));
|
向路由组件传递 state 参数
首先定义路由参数,Link 组件的 to 要定义成一个对象,Route 组件无需接收参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| {}
<Link to={{
pathname: '/home/message/detailed',
state: {
id: item.id,
title: item.title,
content: item.content
}
}}>
{item.title}
</Link>
{}
<Route path="/home/message/detailed" component={Detailed}></Route>
|
然后在 Detailed 组件中从 props.location.state 身上解构赋值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Detailed extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props);
const { id, title, content } = this.props.location.state || {}
return (
<div>
<p>id:{id}</p>
<p>title:{title}</p>
<p>content:{content}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
|
这种传参方式不会再浏览器地址上体现参数,如下所示

路由的push模式和replace模式
在 Link 组件上添加 replace 属性即可开启 replace 模式
1
2
3
4
| {}
<Link to={{pathname: '/home/message/detailed',state: {id: item.id}}} replace>
{item.title}
</Link>
|
开启点击跳转不会压入栈中,而是替换当前路由,不会留下历史记录
开启 replace 的效果

不开启的效果

编程式路由
push 模式传递 params 参数
1
| this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detailed/${id}/${title}/${content}`)
|
push 模式传递 search 参数
1
| this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detailed?id=${id}&title=${title}&content=${content}`)
|
push 模式传递 state 参数
1
2
3
| this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detailed`, {
id, title, content
})
|
replace 模式传递 params 参数
1
| this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detailed/${id}/${title}/${content}`)
|
replace 模式传递 search 参数
1
| this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detailed?id=${id}&title=${title}&content=${content}`)
|
replace 模式传递 state 参数
1
2
3
| this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detailed`, {
id, title, content
})
|
goBack 返回
1
| this.props.history.goBack()
|
goForward 前进
1
| this.props.history.goForward()
|
go 跳转至指定级别
1
2
3
4
5
|
this.props.history.go(2)
this.props.history.go(-2)
|
withRouter 的使用
我们上面使用的路由方法都是在路由组件中使用的,那么在一般组件组件中能否使用 history 对象身上的方法呢?添加相关代码,在 Header 组件中添加

结果如图所示,报错了

这是因为,一般组件并没有接收到 props 参数,而且 props 参数中也没有 history 属性,所以无法使用路由功能。我们可以通过引入 withRouter 方法来让一般组件拥有路由方法
首先引入 withRouter
1
2
|
import { withRouter } from "react-router-dom"
|
然后再导出的地方修改
1
2
|
export default withRouter(Header)
|
结构如图

此时一般组件就拥有了路由功能,现在我们再次点击按钮功能就可以正常使用了

第十三章 AntdUI的使用
快速上手
安装
修改 App.js ,引入 antd 的按钮组件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Button } from 'antd';
import './App.css';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Button type="primary">Button</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
|
修改 src/App.css,在文件顶部引入 antd/dist/antd.css
1
| @import '~antd/dist/antd.css';
|
按需引入
上面的引入方式在 App.js 文件中引入 antd 的全部样式组件,压缩后仍会有 60kb 的大小,但是我们并不会用到全部组件,所以接下来我们来配置按需加载组件
首先安装依赖包
1
| npm i react-app-rewired customize-cra --save
|
修改 package.json
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| /* package.json */
"scripts": {
"start": "react-app-rewired start",
"build": "react-app-rewired build",
"test": "react-app-rewired test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
},
|
然后在项目根目录创建一个 config-overrides.js 用于修改默认配置。
1
2
3
4
| module.exports = function override(config, env) {
return config;
};
|
使用 babel-plugin-import,babel-plugin-import 是一个用于按需加载组件代码和样式的 babel 插件(原理),现在我们尝试安装它并修改 config-overrides.js 文件。
1
| npm i babel-plugin-import --save
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const { override, fixBabelImports } = require('customize-cra');
module.exports = override(
fixBabelImports('import', {
libraryName: 'antd',
libraryDirectory: 'es',
style: 'css',
}),
)
|
然后移除前面在 src/App.css 里全量添加的 @import '~antd/dist/antd.css';
现在我们引入的组件会自动变成按需加载。
引入Icon组件
默认下载的 antd 没有包含 Icon 组件库,所以我们在引入图标时不会显示,我们要单独安装
1
| npm install --save @ant-design/icons
|
使用
1
2
3
4
5
| import { StarOutlined, StarFilled, StarTwoTone } from '@ant-design/icons';
<StarOutlined />
<StarFilled />
<StarTwoTone twoToneColor="#eb2f96" />
|
自定义主题
安装
1
| npm install @craco/craco craco-less --save
|
修改 package.json
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
"scripts": {
- "start": "react-scripts start",
- "build": "react-scripts build",
- "test": "react-scripts test",
+ "start": "craco start",
+ "build": "craco build",
+ "test": "craco test",
}
|
然后在项目根目录创建一个 craco.config.js 用于修改默认配置
把 src/App.css 文件修改为 src/App.less,然后修改样式引用为 less 文件。
1
2
3
|
- import './App.css';
+ import './App.less';
|
1
2
3
|
- @import '~antd/dist/antd.css';
+ @import '~antd/dist/antd.less';
|
修改 craco.config.js 文件如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| const CracoLessPlugin = require('craco-less');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
{
plugin: CracoLessPlugin,
options: {
lessLoaderOptions: {
lessOptions: {
modifyVars: { '@primary-color': '#1DA57A' },
javascriptEnabled: true,
},
},
},
},
],
};
|
这里利用了 less-loader 的 modifyVars 来进行主题配置,变量和其他配置方式可以参考 配置主题 文档。修改后重启 yarn start,如果看到一个绿色的按钮就说明配置成功了。
注意,这种方式已经载入了所有组件的样式,不需要也无法和按需加载插件 babel-plugin-import 的 style 属性一起使用。
第十四章 redux 的使用
什么是 redux
- redux是一个专门用作状态管理的js库,不是react插件库
- 它可以用在react、vue、angular 中,但是用在 react 中的最多
- 作用:集中式的管理 react 中多个组件共享的状态
什么情况下需要用到 redux
- 某个组件的状态需要让其他组件随时获取到(共享)
- 一个组件需要改变另外一个组件的状态(通信)
- 总体原则:能不用就不用,但是不用的话感到困难,那么就用
redux 工作原理

- 首先组件将状态告诉 ActionCreators ,说明自己要干什么事,具体的数据有哪些
- 然后 ActiveCreateors 会把状态打包 dispatch 分发给 Store
- 之后 Store 拿着加工好的数据给 Reducers ,给的中间会把旧的状态和要做的事情一并交给 Reduces 加工
- Reduces 加工好后会返回新的状态交给 Store
- 之后组件通过 getState 从 Store 获取最新的状态
redux 三个核心概念
action
- 动作的对象
- 包含两个属性
- type:标识属性,字符串类型且唯一,必要属性
- data:数据属性,值可以是任意类型,可选属性
- 例子:
{type:'Add',data:2}
reduce
- 用于初始化状态,加工状态
- 加工时,根据旧的 state 和 action,产生新的 state 纯函数
- reduce本质是一个函数,第一次调用时是由 store 自动触发的,传递的 preState 是一个 undefined,action 中的 type 是随机的初始值
store
- 将 state、action、reduce 联系起来的对象
- store.getState() 获取最新状态
- store.dispatch() 分发状态,来告诉 reduce 方法更新状态
- store.subscribe() 监听状态更新方法,只要 reduce 返回了新的状态就会触发这个方法
redux 求和精简版
安装
新建 src\redux\store.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import count_reduce from './count_reduce'
export default createStore(count_reduce)
|
新建 src\redux\count_reduce.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
const initState = 0
export default function reduces(preState = initState, action) {
const { type, data } = action
switch (type) {
case 'add':
return preState + data
case 'subtract':
return preState - data
default:
return preState
}
}
|
在 Count.jsx 组件中使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Space, Select, Button, Typography } from 'antd';
import store from "../redux/store"
const { Option } = Select;
const { Title } = Typography;
export default class Count extends Component {
state = {
selectVal: 1
}
handleChange = (value) => {
this.setState({
selectVal: +value
})
}
add = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
store.dispatch({
type: "add",
data: selectVal
})
}
subtract = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
store.dispatch({
type: "subtract",
data: selectVal
})
}
addIfOdd = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
if (store.getState() % 2 !== 0) {
store.dispatch({
type: "add",
data: selectVal
})
}
}
componentDidMount() {
store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({})
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>
{/* store.getState() 从redux中获取数据 */}
<Title level={4}>当前数据和:{store.getState()}</Title>
</div>
<div>
<Space size='small'>
<Select defaultValue={this.state.selectVal} onChange={this.handleChange}>
<Option value="1">1</Option>
<Option value="2">2</Option>
<Option value="3">3</Option>
</Select>
<Button type="primary" onClick={this.add}>加</Button>
<Button type="primary" onClick={this.subtract}>减</Button>
<Button type="primary" onClick={this.addIfOdd}>奇数加</Button>
</Space>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
|
效果

redux中的状态发生改变后,不会自动帮我们重新渲染页面,需要我们手动调用 this.setState({}) 重新渲染 DOM。
redux 求和完整版
首先新建 src\redux\constant.js
1
2
3
|
export const ADD = 'add'
export const SUBTRACT = 'subtract'
|
接着新建 src\redux\count_action.js
1
2
3
4
5
| import { ADD, SUBTRACT } from "./constant"
export const addAction = (data) => ({ type: ADD, data: data })
export const subtractAction = (data) => ({ type: SUBTRACT, data: data })
|
修改 src\redux\count_reduce.js

对应的我们在 Count 组件中作出相应的修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| + import { addAction, subtractAction } from '../redux/count_action'
add = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
store.dispatch(addAction(selectVal))
}
subtract = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
store.dispatch(subtractAction(selectVal))
}
addIfOdd = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
if (store.getState() % 2 !== 0) {
store.dispatch(addAction(selectVal))
}
}
|
效果是和之前一样的。
异步 action
安装
1
| npm i redux-thunk --save
|
修改 store.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import count_reduce from './count_reduce'
import thunk from "redux-thunk"
export default createStore(count_reduce, applyMiddleware(thunk))
|
- 从
redux 中增加引入 applyMiddleware 函数
createStore 方法增加第二个函数 applyMiddleware(thunk)
修改 count_action.js ,增加一个异步 action
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
export const addAsyncAction = ((data, time) => {
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(addAction(data))
}, time)
}
})
|
使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import store from "../redux/store"
import { addAsyncAction } from '../redux/count_action'
addIfAsync = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
store.dispatch(addAsyncAction(selectVal, 500))
}
|
总结:
第十五章 react-redux 使用
什么是 react-redux
react-redux 是 React 官方推出的一个用于公共状态管理的工具
react-redux 工作原理图

创建容器组件
安装 react-redux
1
| npm install react-redux --save
|
新建 src\container\Count.jsx,作为 Count 的容器组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import Count from "../pages/Count"
import { connect } from "react-redux"
export default connect()(Count)
|
然后在用到 Count UI组件的地方,将引用路径更换为 Count 的容器组件,同时引入 store 作为 props 参数传递给容器组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import Count from './container/Count';
import store from "./redux/store"
render(){
return <Count store={store}/>
}
|
之后将UI组件中所有关于原本的 redux 的操作删除掉即可,重新启动项目,页面正常显示

现在我们就得到了一个容器组件。
容器组件给UI组件传递props
修改容器组件 src\container\Count.jsx
容器组件中的 connect 方法第一次调用可以传递两个参数,两个参数都是一个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
import Count from "../pages/Count"
import { connect } from "react-redux"
import { addAction, subtractAction, addAsyncAction } from "../redux/count_action"
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {
count: state
}
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
addAction: (value) => dispatch(addAction(value)),
subtractAction: (value) => dispatch(subtractAction(value)),
addAsyncAction: (value, time) => dispatch(addAsyncAction(value, time))
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Count)
|
然后再UI组件中通过 props 获取从容器组件传递过来的值
1
2
3
4
| addIfAsync = () => {
const { selectVal } = this.state
this.props.addAsyncAction(selectVal, 1000)
}
|
修改完成后效果一致。
mapDispatchToProps 简写
可以写成下面这种形成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
const mapDispatchToProps = {
addAction,
subtractAction,
addAsyncAction
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Count)
|
状态改变自动渲染页面
使用了 react-redux 后,在 index.js 中添加的监听状态改变的方法就不需要写了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| - import store from "./redux/store"
- store.subscribe(() => {
- ReactDOM.render(
- <BrowserRouter>
- <App />
- </BrowserRouter>,
- document.getElementById("root")
- );
- })
|
我们改变 redux 中的状态后页面仍然会刷新,这是因为在 connect 方法中替我们完成了页面监听的功能。
Provider 组件使用
之前我们需要在容器组件上一个个的添加 store 参数,如果容器组件多的话,就需要写多个 store={store} 的props参数传递
有了 Provider 组件后我们就不要再容器组件上一个一个添加 store 了,它会自动帮我们分析全局的容器组件,我们只需要传一次 store 参数即可
修改 src/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { Provider } from "react-redux"
import store from "./redux/store"
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
|
把我们原来在容器组件上添加的 store 参数去掉,查看效果和之前一致。
将容器组件和UI组件二合一
上面的写法中我们将容器组件和UI组件分成了两个文件去写,这样当我们的组件比较多的时候文件定义就会比较乱,所以我们可以通过如下写法,将两个组件合成一个组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Button, Typography } from 'antd';
import { connect } from "react-redux"
import {addAction} from "../redux/count_action"
const { Title } = Typography;
const mapState = state => {
return {
count: state
}
}
const mapDispatch = {
addAction
}
class ExerciseCount extends Component {
addCount = () => {
this.props.addAction(1)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Title level={4}>当前的和为:{this.props.count}</Title>
<Button type='primary' onClick={this.addCount}>点我加1</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default connect(mapState, mapDispatch)(ExerciseCount)
|
combineReducers 方法合并多个 reducer
之前我们在 store 中只添加了一个 reduce,当我们多个组件都需要用到 redux 时,无法同时传递多个,我们可以借助 combineReducers 方法来实现在 store 中同时连接多个 reducer
修改 store.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers } from 'redux'
import count_reduce from './reduces/count'
import person_reduce from './reduces/person'
import thunk from "redux-thunk"
const allReduces = combineReducers({
count: count_reduce,
persons: person_reduce
})
export default createStore(allReduces, applyMiddleware(thunk))
|
从 redux 增加 combineReducers 方法导出,然后调用 combineReducers,传递一个 reducer 对象作为参数,这个方法的返回值作为 createStore 方法的第一个参数。另外给 combineReducers 方法传递的对象就会作为 redux 中保存数据的 kye value。因此我们在通过 redux 取值时也要修改为 key value 的形式来取值。
纯函数
- 一类特别的函数,只要输入同样的参数,必定会得到同样的输出
- 必须遵守以下的约定
- 不得改写参数数据
- 不会产生副作用,例如网络请求,输入和输出等
- 不能调用如 Date.now() 或者 Math.random() 等不纯的方法
- redux 的 reducer 函数必须是一个纯函数
redux 开发者工具
首先在浏览器搜索并安装插件

然后再我们的项目中安装
1
| cnpm i redux-devtools-extension --save
|
修改 store.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import { composeWithDevTools } from "redux-devtools-extension"
......省略其他代码
export default createStore(allReduces, composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(thunk)))
|
然后打开浏览器,打开控制台即可查看 redux 中存储的所有状态值

抽离 reduce 引入文件
当我们有个reduce 需要引入时,如果全部放在 store.js 文件中,这个文件会变得很难看,所以我们要单独写一个专门用于汇总 reduce 的文件
新建 src\redux\reduces\index.js 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import count from "./count"
import persons from "./person"
import { combineReducers } from "redux"
export default combineReducers({
count,
persons
})
|
然后修改 store.js ,将原本引入的 reduce删除,替换为汇总完的文件即可。完整版的 store.js 代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import allReduces from "../redux/reduces"
import { composeWithDevTools } from "redux-devtools-extension"
import thunk from "redux-thunk"
export default createStore(allReduces, composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(thunk)))
|
第十六章 项目打包和预览
打包和预览
打包执行命令
打包完毕后会提示我们执行如下命令

我们执行这个命令前需要全局安装 serve
serve 可以让我们的任意文件夹变成服务器的根目录,可以帮助我们实现打包后的项目的快速预览
打包完毕后的 -s 可以省略不输入,直接输入 serve build 即可查看项目

配置打包目录
默认打包出来我们需要吧打包文件放在服务器的根目录下使用,但是有时候我们需要吧文件放在二级目录下。这时我们需要修改 package.json 文件

再配置文件内添加 homepage 属性,声明二级菜单的名称即可
第十七章 React 扩展
setState 的两种写法
1.对象式 setState
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
this.setState({ count: count + 1 },()=>{
console.log('更新后的的count:' + this.state.count);
})
|
2.函数式 setState
第一个传递的是一个返回值是状态改变的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
this.setState((state,props) => {
console.log(props);
return {
count: state.count + 1
}
}, () => {
console.log('更新后的的count:' + this.state.count);
})
|
路由懒加载
当我们需要显示某个组件时再去加载某个组件,以缓解第一次加载页面时的压力。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
import React, { Component, lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
import { NavLink, Route, } from "react-router-dom"
import "./router.css"
import Loading from "./Loading"
const Home = lazy(() => import("./Home"))
const About = lazy(() => import("./About"))
export default class index extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>
<NavLink to="/home" style={{ "marginRight": "20px" }}>Home</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/about">About</NavLink>
</div>
<hr />
<div>
{/* 使用 Suspense 组件报告路由组件,fallback 属性定义等待加载期间显示的组件 */}
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
</Suspense>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
|
- 从 react 中引入自带的 lazy 方法和 Suspense 组件
- 修改路由组件的引入方式
const Home = lazy(() => import("./Home"))
- 使用 Suspense 组件报告路由组件,fallback 属性定义等待加载期间显示的组件
fallback={<Loading />
这样修改后组件只会在需要时被加载,加载过的组件在第二次显示时不会二次加载

stateHooks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import react from "react"
function stateHooks(){
const [count,setCount] = react.useState(0)
const [name,setName] = react.useState('Tome')
function add(){
setCount(count+1)
}
function changeName(){
setName(preName=>preName='Juar')
}
return (
<div>
<h2>当前的数据和为:{count}</h2>
<h3>我的名字是:{name}</h3>
<button onClick={add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={changeName}>修改名字</button>
</div>
)
}
export default stateHooks
|
react.useState 方法可以让我们在函数式组件中使用 stat,这个返回接收一个初始值,返回一个两位数的数组。数组第一位是这个初始化值的名称,第二位是修改这个值的方法。
在第一次useState后回缓存count,点击修改会重新调用当前的函数,但是不会更改count的值。
useEffect
useEffect 方法可以在函数式组件中模拟声明周期的一个钩子函数。它接收两个参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| import react from "react"
import ReactDom from "react-dom"
function stateHooks() {
const [count, setCount] = react.useState(0)
const [name, setName] = react.useState('Tome')
react.useEffect(() => {
let timer = setInterval(() => {
setCount(count=>count+1)
}, 1000);
return ()=>{
clearInterval(timer)
}
}, [])
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
}
function changeName() {
setName(preName => preName = 'Juar')
}
function unmont(){
ReactDom.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('root'))
}
return (
<div>
<h2>当前的数据和为:{count}</h2>
<h3>我的名字是:{name}</h3>
<button onClick={add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={changeName}>修改名字</button>
<button onClick={unmont}>卸载组件</button>
</div>
)
}
export default stateHooks
|
useEffect 方法的几种状态
- 只传入一个函数,则表示监听了所有
stateValue 值的变化,只要有值发生改变就会触发传入的函数。相当于 componentDidUpdate 函数
- 传递一个空的数组,不会监听任何值的改变,只会在组件第一次加载时触发。相当于
componentDidMount
- 当传入的函数返回一个函数时,会在组件销毁前出发,因此返回的函数相当于
componentWillUnmount
useRef
useRef 可以让我们在函数式组件中使用 ref 获取输入框的值,用法于类式组件中的 createRef 一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import React from "react"
function Demo(){
const myInput = React.useRef()
function getInputVal(){
console.log(myInput.current.value);
}
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={myInput}/>
<button onClick={getInputVal}>获取输入框的值</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Demo
|
Fragment
当我们不得不指定一个 div 标签的时候,可以使用 Fragment 来包裹页面元素,然后 react 在渲染的时候不会去渲染 Fragment 标签,从而来优化我们的页面结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import React,{Fragment} from "react"
function Demo(){
return (
<Fragment>
<input type="text" />
<input type="text" />
</Fragment>
)
}
export default Demo
|
渲染后的页面
1
2
| <input type="text">
<input type="text">
|
createContext
在多级组件嵌套时我们可以通过 context 来跨级传递参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import "./index.css"
const myContext = React.createContext()
const { Provider, Consumer } = myContext
export default class A extends Component {
state = {
name: "Tome",
age: 10
}
render() {
const { name, age } = this.state
return (
<div className='root'>
<h2>我是A组件</h2>
<div>我的名字是:{name},我的年龄是:{age}</div>
<Provider value={{ name, age }}>
<B />
</Provider>
</div>
)
}
}
class B extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='child'>
<h2>我是B组件</h2>
<C />
</div>
)
}
}
class C extends Component {
static contextType = myContext
render() {
console.log(this.context);
const { name, age } = this.context
return (
<div className='grid'>
<h2>我是C组件</h2>
<div>我从A组件接收到的名字是:{name},年龄是:{age}</div>
<D />
</div>
)
}
}
function D() {
return (
<div className='grid2'>
<h2>我是D组件</h2>
<div>我从A组件接收到的名字是:
{/* 在函数式组件中的使用方法 */}
<Consumer>
{
context => {
const { name, age } = context
return `${name},年龄是:${age}`
}
}
</Consumer>
</div>
</div>
)
}
|
PureComponent
我们做组件优化时,如果状态没有发生改变,则不应该重复调用 render 函数进行重复渲染。我们可以修改组件继承自 PureComponent,它在底层做了优化,只有状态在真正发生改变时才会触发 render 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import "./index.css"
export default class index extends PureComponent {
state = {
carName:'奔驰c63'
}
changeCar = ()=>{
this.setState({
carName:'迈巴赫'
})
}
render() {
console.log('更新触发');
return (
<div className='parent'>
<h4>我的车是:{this.state.carName}</h4>
<button onClick={this.changeCar}>点击换车</button>
<B />
</div>
)
}
}
class B extends PureComponent{
render(){
console.log('子组件render');
return(
<div className='child'>
我是子组件
</div>
)
}
}
|
propsRender
通过函数调用的形式,向组件内动态传入带内容的解构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import "./index.css"
export default class index extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='parent'>
<h2>propsRender</h2>
{/* render 等于一个函数,返回一个组件,接收到参数传递给子组件 */}
<A render={(carName) => <B carName={carName} />}></A>
</div>
)
}
}
class A extends Component {
state = {
carName: "奔驰"
}
render() {
const { carName } = this.state
return (
<div className='child1'>
我是A组件<br />
我的汽车是:{carName}
{/* 在A组件中调用props上的render方法渲染返回的组件并传递参数 */}
{this.props.render(carName)}
</div>
)
}
}
class B extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='child2'>
我是B组件<br />
从A组件接收到的名字是:{this.props.carName}
</div>
)
}
}
|

错误边界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Child from "./Child"
export default class Parent extends Component {
state = {
hasError: null
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
console.log('@@', error);
return {
hasError: true
}
}
componentDidCatch(){
console.log('发生了错误,通知服务器');
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ "border": '1px solid #ddd', "padding": "20px" }}>
<h2>我的Parent组件</h2>
{/* 判断错误是否存在,来显示不同的组件。避免一个错误影响全局页面 */}
{this.state.hasError ? <h4>网络异常,请稍后重试</h4> : <Child />}
</div>
)
}
}
|
注意:该功能只能在生产环境下有效。本地开发环境不生效。
组件间通信方式总结
组件间的关系
- 父子组件
- 兄弟组件(非嵌套组件)
- 祖孙组件(跨级组件)
几种通信方式
- props
- children props
- render props
- 消息订阅、发布
- 集中式状态管理
- conText
比较好的搭配方式
- 父子组件:props
- 兄弟组件:消息订阅、集中式状态管理
- 祖孙组件:消息订阅、集中式状态管理、conText
js相关复习
类的创建和继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class Person{
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
speak(){
console.log(`我叫${this.name},几年${this.age}岁了`);
}
}
const p1 = new Person("张三",19)
p1.speak()
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name,age,grade){
super(name,age)
this.grade = grade
}
speak(){
console.log(`我叫${this.name},几年${this.age}岁了,今年上${this.grade}`);
}
}
const s1 = new Student('lisi','18','高一')
s1.speak()
|
展开语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
let a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(...a);
let b = [6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log([...a, ...b]);
function sum(...numbers) {
console.log(numbers);
return numbers.reduce((a, b) => {
return a + b
}, 0)
}
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3));
console.log(sum(3));
let person = {
name: "Tom",
age: 19,
classInfo: {
height: 180
}
}
let person2 = {
...person
}
person.name = "jery"
person.classInfo.height = 190
console.log(person2);
console.log(person);
|
.png)